The evolution of the space industry: trends and technologies
The aerospace sector is in the midst of the fourth industrial revolution, Space 4.0. This era is characterised by the entry of new private players which give a competitive, dynamic and flexible commercial boost to the market.
Players such as SpaceX, Google, Facebook, Amazon, Microsoft and Virgin are examples of new entrants in a sector previously reserved for public institutions, bringing greater integration of digital technologies.
The ecological transition also influences and characterises the Space 4.0 era, driving interest not only towards technological innovation research, but also towards sustainable practices and materials to reduce the environmental impact of space activities, such as the development of reusable rockets and hybrid engines.
A critical success factor of the Space Economy will certainly be determined by the availability of economic resources by the involved subjects.
Up to now, the efforts of the major players are in fact focused on affordability to enable the development of the Space Economy in particular through new ground infrastructures (launch bases, spaceports). These infrastructures are not only starting points for launchers, but offer engineering, logistics, recovery and reconditioning, and operational support services. For example, at Grottaglie in Apulia, the construction of the first spaceport in Italy focused on suborbital transport is underway: a type of space mission in which a vehicle crosses the boundary line of the Earth's atmosphere without reaching the speed necessary to remain in orbit around the Earth, and therefore has a natural return to Earth dictated by physical laws.
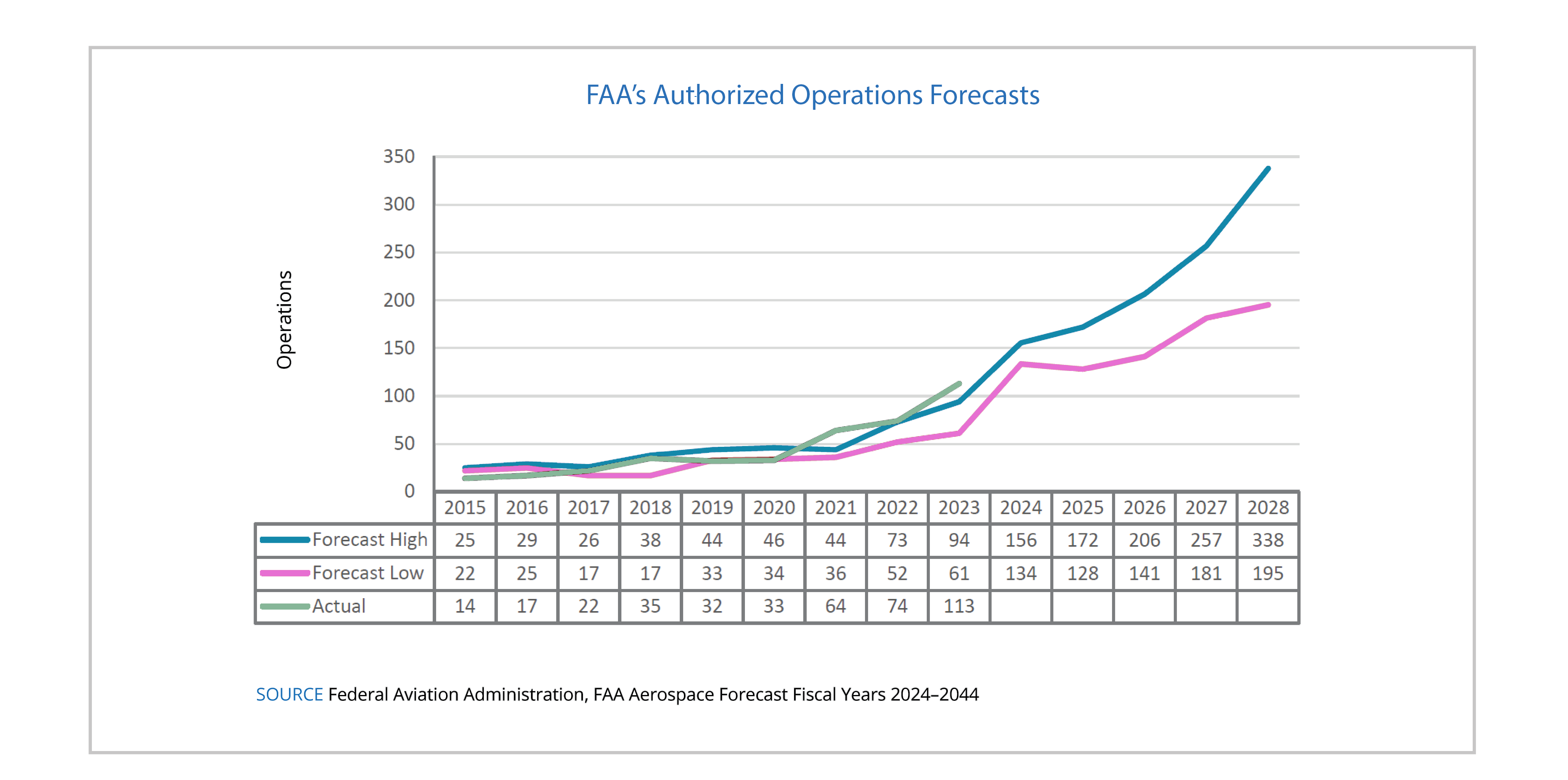
The expansion of ground infrastructure and the evolution of launchers have created an ideal environment for the growth of the launch operations market, as shown in the graph with past and forecast data of Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) authorised operations.

AEROSPACE TECHNOLOGIES APPLIED TO DIFFERENT SECTORS
As well known, the investments required in the aerospace sector are high, there are complex regulatory aspects, and market volatility must be addressed to achieve positive results in the medium to long term. On the other hand, the positive impacts go far beyond the boundaries of the space industry itself, showing it to be a sector that encourages progress. The technologies developed for space exploration are in fact used in various industrial sectors.
Of particular interest is the satellite telecommunication technology segment, which today acts as a complement to terrestrial networks (cable, fibre, copper, FWA, 5G). According to Analysys Mason, satellite telecommunications turnover will grow by USD 32.5 billion by 2027, with a market in 2023 estimated at USD 41.37 billion according to The Business Research Company.
Below are concrete examples of aerospace technologies applied in the agrifood, mobility and biotech sectors.

AGRIFOOD: PRECISION AGRICULTURE AND NEW TECHNOLOGIES
Earth Observation (EO) and satellite navigation (GNSS) technologies can be used to optimise irrigation, fertiliser and pesticide use. Vegetation and reflectance indices can also be derived from satellite images, identifying the stress and physical characteristics of plants. The use of such technologies also enables better utilisation of land and optimisation of the resources used, while also allowing emissions to be controlled.
PRECISION AGRICULTURE WITH DRONES: WHAT IT IS AND PRACTICAL EXAMPLES
Not only satellites, but also drones (supported by satellite geolocation networks) are used to support precision agriculture. They can acquire detailed images and topographical data to analyse soil drainage, thus integrating satellite data to then apply and distribute pesticides and fertilisers in a targeted manner.
A further meeting point between agri-food technology and the space economy can be found in research dedicated to increasing the shelf life of food supplies for astronauts on missions by at least twenty months and ensuring their nutritional quality.
MOBILITY AND TOURISM: FROM AUTONOMOUS DRIVING TO URBAN AIR MOBILITY
Satellite geo-positioning systems are useful tools in the development of self-driving vehicles, to ensure their safety and road monitoring.
Other innovative technologies in connection with the space economy are, for example, air taxis and indoor positioning technologies, the former are designed to take off and land vertically, while the latter operate in transport nodes such as airports, railway stations and bus terminals. In some States, zones have been defined where self-driving and air-mobile vehicles will be able to circulate. These technologies are an example of integration between space-source data and automated driving algorithms.
In the tourism sector, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) enable the creation of dynamic maps that report real-time data such as air quality, snow depth, and current weather events. Satellite networks also provide connectivity and support services in areas with poor traditional network coverage.
HEALTH AND BIOTECH: FROM TELEMEDICINE TO NEW THERAPIES
The growing burden on national healthcare systems calls for a shift to a mixed care model, with an increasing role for telemedicine and home care, hence the need for broadband satellite communications coverage.
In the field of prevention, new mobile applications of public interest are being developed such as, for example, UV-ray monitoring, which uses the capabilities of the Copernicus satellite programme to receive information on the amount of UV rays present at the time.
Interesting developments in the medical field relate to the physical challenges astronauts face in the space habitat, the absence of gravity for example causes loss of bone mass. Studies and research applied to space may also open up new avenues for medical applications aimed at citizens.
Trends in this area, new lifestyles and needs lead to the development of new products and services, generating new business for companies.
Intesa Sanpaolo's IMI Corporate & Investment Banking Division has always followed the evolution of the Space Economy from the very beginning. We support our customers involved in this sector, particularly in the Automotive & Industrials, Healthcare, Telecom, Media & Technology industries.
NOTE For additional information:: X-Plore Spacetech